Arduino Frequency Counter Library
참고 : http://interface.khm.de/index.php/lab/experiments/arduino-frequency-counter-library/
Download >FreqCounter Library
Example Programm
#include <FreqCounter.h>
void setup() {
Serial.begin(57600); // connect to the serial port
Serial.println("Frequency Counter");
}
long int frq;
Void loop() {
FreqCounter::f_comp= 8; // Set compensation to 12
FreqCounter::start(100); // Start counting with gatetime of 100ms
while (FreqCounter::f_ready == 0) // wait until counter ready
frq=FreqCounter::f_freq; // read result
Serial.println(frq); // print result
delay(20);
}
Preamplifier schematics
Source Codes
Updated 10/2010 ; works with atmega328; removed some glitches
Updated 1/2012 ; Arduino 1.0
Download >FreqCounter Library
Forum
further questions to this topic can be discussed here:
http://arduino.cc/forum/index.php/topic,64219.0.html
http://www.arduino.cc/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1231326297
참고 : http://www.electronicsblog.net/arduino-frequency-counterduty-cycle-meter/
This meter gives the best results at 0 – 1000 Hz range. It works by measuring square wave total and high period duration using 16 bit hardware counter.
음,, 1Khz까지 밖에 안되나?
attachInterrupt()
Description
Specifies a named Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) to call when an interrupt occurs. Replaces any previous function that was attached to the interrupt. Most Arduino boards have two external interrupts: numbers 0 (on digital pin 2) and 1 (on digital pin 3). The table below shows the available interrupt pins on various boards.
| Board | int.0 | int.1 | int.2 | int.3 | int.4 | int.5 |
| Uno, Ethernet | 2 | 3 | ||||
| Mega2560 | 2 | 3 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 |
| Leonardo | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 7 | |
| Due | (see below) | |||||

As you may know frequency = 1/Period and Duty Cycle = High period duration/total period duration.
Square wave signal is connected to Arduino Mega 21 pin, because this pin is input for external interrupt.
External interrupt from rising edge is enabled.
void setup() { lcd.begin(16, 2); pinMode(Button, INPUT); digitalWrite(Button, HIGH); //pull up resistor TIMSK1=0x01; // enabled global and timer overflow interrupt; TCCR1A = 0x00; // normal operation page 148 (mode0); attachInterrupt(2, interrupt, RISING); }
x=0) Signal period’s beginning – rising edge triggers external interrupt. Counter value is saved to variable “count”, it contains measurement of signal total period. 16 bit counter is started (again from zero), but now external interrupt is set to be triggered by falling edge.
x=1) When falling edge occurs counter value is saved to variable “middle” , it contains measurement of signal high period. External interrupt is set to be triggered by rising edge.
void interrupt() { if (!x) { count=TCNT1; TCNT1=0x000; TCCR1B=prescaler; attachInterrupt(2, interrupt, FALLING); } else { middle=TCNT1; attachInterrupt(2, interrupt, RISING); } x=~x; }
Frequency counter for better accuracy have automatic 16 bit counter clock prescaler. Prescaler sets counter’s speed.
- If speed is to high counter may overflow till signal period is ended
- If speed is to low only small part of counter range’s(0-65536) is used, it cause reduced measurement accuracy.
Program increase prescaler(clock frequency divider) if counter overflow appears.
int divider[6] ={ 0,1,8,64,256,1024}; int prescaler=5;
ISR(TIMER1_OVF_vect) {
if (prescaler<4) {
prescaler++;
}
}
In case only small smart part of counter range is used prescaler is reduced if it’s possible.
if (prescaler>1) { if (usage<0.15) { prescaler--; delay(200); } }
Meter in action:
You can see that accuracy is decreasing when frequency increases, because counter speed is to low. DSO Nano v2 oscilloscope was used as signal source.
Full program:
//Arduino frequency counter/duty cycle meter //www.electronicsblog.net/ #include <LiquidCrystal.h> LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2); #define Button 52 int divider[6] ={ 0,1,8,64,256,1024}; int prescaler=5; int b=0; int screen =0; double count =0; double middle =0; double usage =0; char x=0; ISR(TIMER1_OVF_vect) { if (prescaler<4) { prescaler++; } } void interrupt() { if (!x) { count=TCNT1; TCNT1=0x000; TCCR1B=prescaler; attachInterrupt(2, interrupt, FALLING); } else { middle=TCNT1; attachInterrupt(2, interrupt, RISING); } x=~x; } void setup() { lcd.begin(16, 2); pinMode(Button, INPUT); digitalWrite(Button, HIGH); //pull up resistor TIMSK1=0x01; // enabled global and timer overflow interrupt; TCCR1A = 0x00; // normal operation page 148 (mode0); attachInterrupt(2, interrupt, RISING); } void loop() { /// screen modes switch (screen) { case 0: lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print(" "); lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("Freq "); lcd.print(16000000.0/divider[prescaler]/count); lcd.print(" Hz"); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); lcd.print("Duty "); lcd.print(middle/count*100); lcd.print(" % "); lcd.print(" "); break; case 1: lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("Period: "); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); lcd.print(0.0000625*divider[prescaler]*count); lcd.print(" ms "); break; case 2: lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("H "); lcd.print(0.0000625*divider[prescaler]*middle); lcd.print(" ms "); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); lcd.print("L "); lcd.print(0.0000625*divider[prescaler]*(count-middle)); lcd.print(" ms "); break; case 3: lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("Prescaler /"); lcd.print(divider[prescaler]); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); lcd.print("Count.use "); usage=count/65536*100; lcd.print(usage); lcd.print("% "); break; } delay(250); if (prescaler>1) { if (usage<0.15) { prescaler--; delay(200); } } ///button ///////// if (!digitalRead(Button)&&!b) { screen++; if (screen==4) { screen=0 ; } lcd.clear(); b=3; }; if (!b==0) b--; }


![00027.MTS_snapshot_00.17_[2011.03.06_18.51.02]](http://www.electronicsblog.net/wp-content/uploads/300x168x00027.MTS_snapshot_00.17_2011.03.06_18.51.02-300x168.jpg.pagespeed.ic.tOdESW3Ge-.jpg)
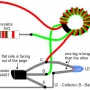
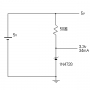
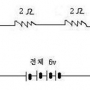
 Joule thief 회로(저전압 승압회로) 실험 결과
Joule thief 회로(저전압 승압회로) 실험 결과
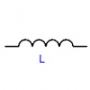
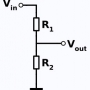
 전자기호
전자기호